Cisco IP PBX: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
2. What is Cisco IP PBX?
3. Key Features of Cisco IP PBX
4. How Cisco IP PBX Works
5. Cisco IP PBX vs. Traditional PBX Systems
6. Cisco IP PBX Architecture
7. Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) Overview
8. Deployment Models of Cisco IP PBX
9. Components of Cisco IP PBX
10. Cisco IP Phones and Endpoints
11. SIP Trunking and PSTN Integration
12. Security Considerations in Cisco IP PBX
13. Cisco IP PBX Licensing and Pricing
14. Benefits of Using Cisco IP PBX
15. Challenges and Limitations
16. Cisco IP PBX Implementation Steps
17. Troubleshooting and Maintenance
18. Use Cases in Different Industries
19. Future of Cisco IP PBX
20. Conclusion
1. Introduction
Cisco IP PBX is a modern telephony solution that enables businesses to handle their voice communications over an IP network. It provides high-quality voice, video, messaging, and mobility features, making it a preferred choice for enterprises, call centers, and government organizations.
This guide explores every aspect of Cisco IP PBX, including its architecture, features, deployment models, and benefits.
2. What is Cisco IP PBX?
A Cisco IP PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is a telephony system that enables voice communication over an IP network rather than traditional phone lines. It is part of Cisco’s Unified Communications solutions, primarily powered by Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM).
Unlike traditional PBX systems that rely on analog or ISDN lines, an IP PBX uses VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) to manage calls, allowing businesses to save costs, improve flexibility, and integrate with various digital services.
3. Key Features of Cisco IP PBX
Cisco’s IP PBX offers a wide range of advanced features, including:
VoIP Call Management – Route and manage voice calls over an IP network.
Unified Messaging – Integrate voicemail, email, and text messaging.
Call Conferencing – Enable multi-party voice and video calls.
Mobile and Remote Access – Connect from any device, anywhere.
Auto Attendant – Automated call routing and handling.
Call Recording and Logging – Track and record calls for compliance.
SIP Trunking – Reduce costs by connecting to SIP-based providers.
Integration with Collaboration Tools – Works with Webex, Microsoft Teams, and more.
4. How Cisco IP PBX Works
Cisco IP PBX operates using the following key components:
1. IP Phones & Softphones – Used by employees to make and receive calls.
2. Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) – The central call-processing system.
3. Voice Gateways – Connects the system to external networks (PSTN, SIP trunks).
4. Media Servers – Manage call features like conferencing and voicemail.
5. Network Infrastructure – Routers and switches ensuring data flow.
When a call is placed, CUCM manages it by determining the best route, applying call policies, and connecting the endpoints efficiently.
Cisco IP PBX vs. Traditional PBX Systems
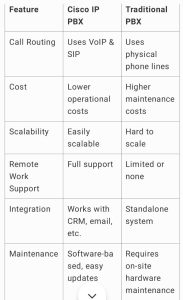
6. Cisco IP PBX Architecture
Cisco’s IP PBX architecture is based on CUCM and includes:
Call Control Layer – Handles call routing, signaling, and policies.
Media Processing Layer – Supports codecs, conferencing, and transcoding.
Application Layer – Provides features like voicemail and video calls.
Endpoints Layer – Includes Cisco IP phones, softphones, and mobile devices.
7. Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) Overview
CUCM is the heart of Cisco IP PBX, responsible for:
Call processing and routing
Device registration and management
Security enforcement
Integration with external services
CUCM supports up to 80,000 users, making it suitable for enterprises of all sizes.
8. Deployment Models of Cisco IP PBX
Cisco IP PBX can be deployed in three main ways:
1. On-Premises – Installed within the company’s network.
2. Cloud-Based (Cisco Webex Calling) – Hosted and managed by Cisco.
3. Hybrid – A mix of on-premises and cloud solutions.
9. Components of Cisco IP PBX
Cisco IP Phones
CUCM Servers
Voice Gateways
SIP Trunks
Call Recording Systems
10. Cisco IP Phones and Endpoints
Cisco offers various IP phone models:
Cisco 7800 Series – Affordable and basic.
Cisco 8800 Series – High-end with HD voice and video support.
Cisco Jabber & Webex App – Softphone applications for mobile and PC users.
11. SIP Trunking and PSTN Integration
SIP trunking enables Cisco IP PBX to connect to external telephone networks, reducing costs compared to traditional PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) lines.
12. Security Considerations in Cisco IP PBX
Encryption (TLS, SRTP)
Firewall & Intrusion Prevention
Authentication & Access Control
Regular Patching & Updates
13. Cisco IP PBX Licensing and Pricing
Cisco offers various licensing models, including:
Perpetual Licensing (CUCM on-premises)
Subscription-Based (Cisco Webex Calling)
User-Based Licensing (Essentials, Enhanced, Premium)
Pricing varies based on the number of users and features needed.
14. Benefits of Using Cisco IP PBX
Cost Savings
Scalability
Remote Work Flexibility
Better Call Quality & Features
15. Challenges and Limitations
High Initial Setup Cost
Requires Network Infrastructure
Regular Maintenance & Updates Needed
16. Cisco IP PBX Implementation Steps
1. Assess Business Needs
2. Choose Deployment Model
3. Set Up Network Infrastructure
4. Install and Configure CUCM
5. Register IP Phones
6. Test and Optimize Performance
17. Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Common issues and solutions include:
Call Quality Problems → Check network bandwidth.
SIP Registration Failure → Verify SIP trunk settings.
One-Way Audio → Check firewall rules.
18. Use Cases in Different Industries
Enterprise Communication
Healthcare (Telemedicine)
Education (Remote Learning)
Call Centers
19. Future of Cisco IP PBX
AI-Driven Call Management
Better Cloud Integration
Enhanced Security Measures
20. Conclusion
Cisco IP PBX is a powerful and flexible communication system for businesses. With its advanced features and scalability, it remains a leading solution in enterprise telephony.
