Network Cabling: The Foundation of Reliable Connectivity
Network cabling is essential for creating robust and efficient communication networks, connecting devices and enabling the transfer of data, voice, and video signals. The right cabling infrastructure ensures high-speed internet connectivity, minimal downtime, and secure data transfer. In this guide, we’ll dive into the fundamentals of network cabling, types of cables, essential components, installation best practices, and some of the leading brands in the industry.
What is Network Cabling?
Network cabling is the physical medium through which data is transmitted across networks, allowing communication between devices like computers, servers, routers, and switches. Proper cabling setup is vital for any business, as it directly impacts network performance, reliability, and scalability.
Importance of Network Cabling
An efficient network cabling system is crucial for various reasons:
- Reliable Data Transfer: Quality cabling reduces data loss and ensures consistent connectivity.
- Speed and Performance: High-quality cables support high-speed data transfer, essential for applications like video conferencing, online gaming, and file sharing.
- Scalability: With the right cabling infrastructure, organizations can easily scale their networks as they grow.
- Reduced Downtime: Structured cabling reduces the likelihood of network disruptions, ensuring that businesses can operate smoothly.
- Enhanced Security: Wired networks are generally more secure than wireless networks, making network cabling a preferable choice for sensitive environments.
Types of Network Cables
Different types of network cables cater to various networking needs. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
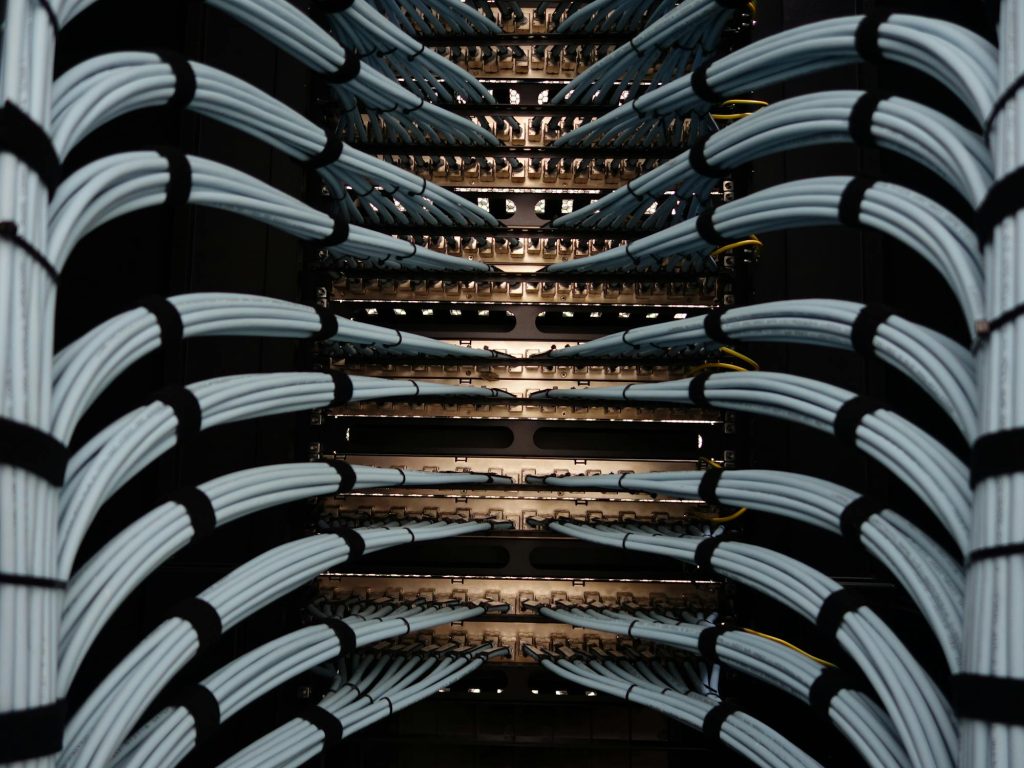
- Ethernet (Twisted Pair) Cables
Ethernet cables are the most widely used network cables, especially in local area networks (LANs). They consist of twisted pairs of wires designed to reduce electromagnetic interference. Ethernet cables come in various categories, each with different data transfer speeds and maximum lengths:
Cat5: Older standard with speeds up to 100 Mbps, mostly phased out in favor of faster cables.
Cat5e: Enhanced version of Cat5, supporting speeds up to 1 Gbps and a maximum length of 100 meters.
Cat6: Supports speeds up to 10 Gbps over short distances (up to 55 meters) and is commonly used in professional setups.
Cat6a: An upgraded version of Cat6, supporting 10 Gbps speeds over 100 meters.
Cat7: Designed for high-performance applications with speeds up to 10 Gbps and improved shielding.
Cat8: The latest standard, supporting speeds up to 40 Gbps over short distances (up to 30 meters), ideal for data centers.
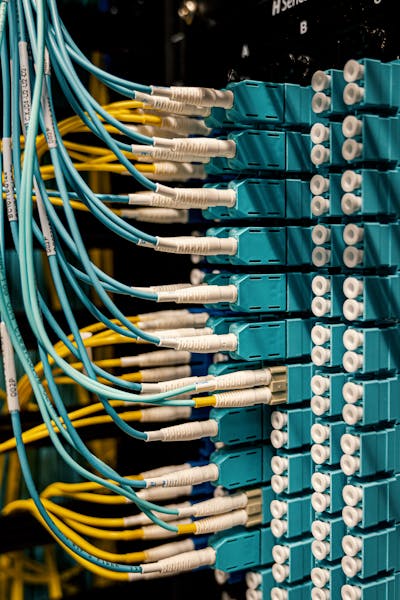
- Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables transmit data as light, offering high-speed, long-distance connectivity with minimal signal loss. They are often used in enterprise settings and data centers due to their speed and reliability. There are two main types of fiber optic cables:
Single-Mode Fiber (SMF): Designed for long-distance communication, SMF has a smaller core and transmits a single light signal, minimizing interference.
Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF): Best for short distances, MMF has a larger core and can carry multiple light signals simultaneously, making it ideal for LANs and data centers.
- Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables are commonly used in older networking setups and cable television. They consist of a single conductor wire surrounded by insulation, shielding, and an outer sheath. Coaxial cables are durable and resistant to interference, but they have largely been replaced by Ethernet and fiber optic cables for high-speed applications. - USB Cables
USB cables are used for short-distance connections, often in home and office setups to connect peripherals like printers and cameras to computers. USB 3.0 and 3.1 offer fast data transfer speeds, but USB is not typically used for large-scale networking. - HDMI Cables
While HDMI cables are primarily used for connecting display devices, they are sometimes used in specialized networks for multimedia data transfer in environments such as AV setups. - Power over Ethernet (PoE) Cables
PoE cables supply power along with data, enabling devices like IP cameras and wireless access points to receive power and data through a single cable. This reduces the need for additional power outlets, making PoE a popular choice in business environments.
Components of a Network Cabling System
A reliable network cabling system consists of more than just cables. Here are some key components:
- Connectors
Connectors join cables to devices, ensuring stable connections. The most common connectors include:
RJ45: Used with Ethernet cables for connecting network devices.
SC, LC, and ST: Common connectors for fiber optic cables, with SC and LC frequently used in data centers.
BNC: Connector for coaxial cables, often used in video applications.
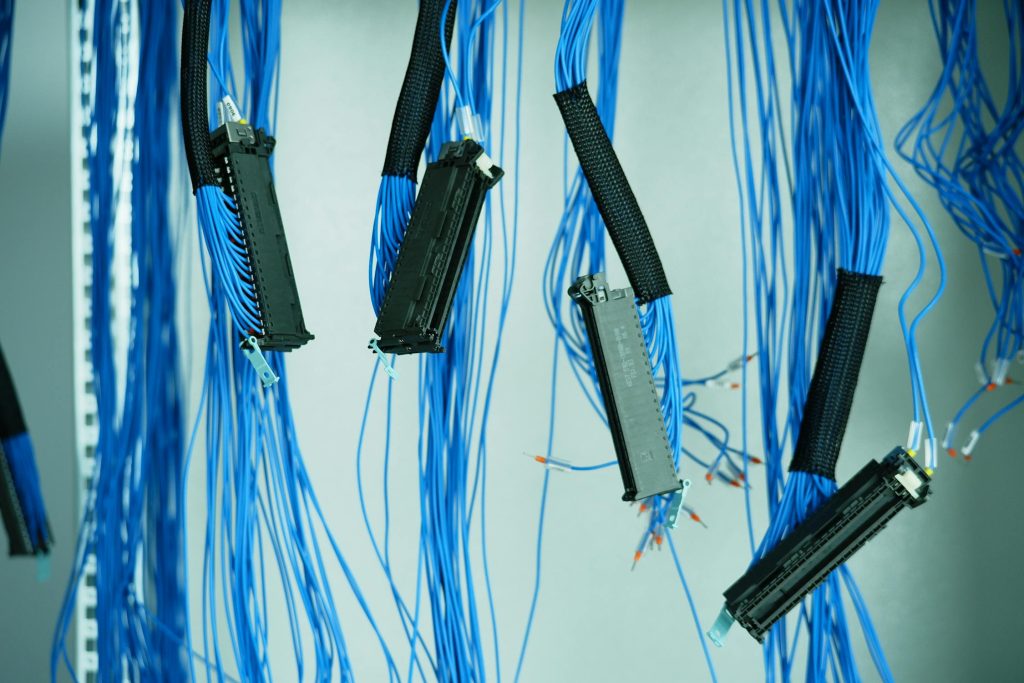
- Patch Panels
Patch panels organize and manage cable connections, making it easy to identify and reroute cables as needed. They’re essential in structured cabling systems for efficient network management. - Cable Management
Cable organizers, such as racks, trays, and cable ties, keep cables organized and prevent tangling, reducing maintenance time and improving network performance. - Switches and Routers
Switches connect multiple devices within a network, while routers manage data traffic between networks. Switches are typically used with Ethernet cables, while routers connect different network types. - Network Jacks and Wall Plates
Wall plates with built-in jacks provide network access points in convenient locations, allowing for a cleaner installation and organized cabling. - Network Interface Cards (NICs)
NICs are installed in computers to enable network connectivity. They serve as the physical interface between the computer and the network.
Network Cabling Installation Best Practices
A well-planned installation process can ensure optimal performance and longevity for network cabling. Here are some essential best practices:
- Conduct a Site Survey
Before installation, conduct a thorough site survey to determine the layout, identify potential obstacles, and assess future scalability needs. - Choose the Right Cable Type
Select cables based on the network’s speed, distance, and reliability requirements. For example, Cat6 or Cat6a cables are ideal for business networks, while fiber optic cables are best for long-distance, high-speed data transfer. - Plan Cable Routes Carefully
Avoid running cables near electrical lines or heavy machinery to minimize electromagnetic interference. Use cable trays and conduits to organize cables neatly. - Follow Structured Cabling Standards
Structured cabling systems, such as those defined by ANSI/TIA standards, provide a systematic approach to cabling, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot. - Use Quality Components
Invest in high-quality connectors, patch panels, and cable management accessories to ensure stable and secure connections. - Test the Installation
After installation, perform cable testing using network testers to ensure each cable meets performance standards. Regular testing also helps identify any potential faults. - Plan for Scalability
Use patch panels and modular connectors to make it easy to expand the network in the future. Leave room in conduits and racks for additional cables as needed. - Label Cables and Connections
Properly label each cable, port, and connector for easy identification, especially in large networks. This helps reduce downtime during maintenance and troubleshooting.
Top Network Cabling Brands
Many brands offer high-quality network cables and components. Here are some of the most popular:
- Belden
Belden is known for its durable Ethernet and coaxial cables, often used in industrial and commercial environments. Belden cables are designed for high-speed data transmission and offer reliable performance. - Panduit
Panduit offers a wide range of structured cabling solutions, including copper and fiber optic cables, connectors, and cable management systems. They’re known for innovation in data center and enterprise solutions. - CommScope
CommScope manufactures a variety of network infrastructure solutions, including SYSTIMAX and NETCONNECT structured cabling systems. They provide high-quality cables for data centers and enterprise networks. - Siemon
Siemon specializes in high-performance cabling solutions, including Cat6A and Cat7 cables, as well as fiber optic systems. Siemon’s products are widely used in data centers and office environments. - Leviton
Leviton offers a broad range of networking products, from Ethernet cables to patch panels and fiber solutions. Their products are popular in residential, commercial, and industrial networks. - Corning
Corning is a leader in fiber optic technology, providing high-quality fiber optic cables and connectivity solutions. Their cables are known for durability and performance, making them ideal for long-distance communication. - General Cable
General Cable offers both copper and fiber optic cables, widely used in commercial and industrial applications. They provide reliable, cost-effective cabling options for large-scale installations. - Hubbell
Hubbell provides structured cabling and data center solutions, including Cat6 and Cat6A cables, patch panels, and connectors. They’re known for quality and compliance with industry standards. - Nexans
Nexans is a global leader in advanced cabling solutions, offering fiber optic and copper cabling for high